
Feasibility of Establishing a Coconut Oil Processing Plant in the Philippines
Overview of the Feasibility Study of Coconut Oil Extraction Project in the Philippines
The coconut oil extraction industry plays a strategic role in the Philippines, contributing nearly 8% of the country’s agricultural exports and employing over 3.5 million coconut farmers. This feasibility study explores the technical and financial aspects of establishing a coconut oil extraction plant in the Philippines, assessing key factors such as market potential, raw material availability, and investment outlook.
The study’s objective is to determine whether a medium-to-large scale extraction facility is viable under current economic conditions. The research covers plant engineering, supply logistics, and operational sustainability, aligning with the national goals of value-added agro-processing.
Market demand for refined, bleached, and deodorized (RBD) coconut oil continues to expand, particularly in India, China, and the EU, where annual imports have surpassed 900,000 tons in 2024. The competitive advantage of Philippine producers lies in the high oil yield of local coconuts—64% oil content—and proximity to major export ports like Batangas and Davao.
The feasibility assessment reveals that with optimized logistics and energy-efficient processing systems, investors can expect a return on investment (ROI) within 3.8 to 4.2 years.
Engage with our industrial consultants to develop your coconut oil plant blueprint tailored for Philippine market conditions and export growth potential.
Raw Material and Supply Chain Analysis: The Coconut Advantage in the Philippines
The Philippines ranks as the second-largest coconut producer worldwide, yielding about 14.8 million metric tons annually across 3.5 million hectares of plantations. Key producing provinces include Quezon, Davao Oriental, and Northern Samar, providing year-round copra supply for oil extraction.
Logistics efficiency is vital. Most raw materials are collected within 50–120 km from plant sites and transported by bulk trucks to processing facilities. Establishing collection hubs near coastal areas reduces average transport cost by 15–18%, ensuring a stable supply chain even during peak export months.
Seasonal fluctuations—usually between May to November—can impact copra moisture levels. Thus, implementing controlled drying systems (maintaining 5–6% moisture) and vendor quality contracts are essential strategies for consistent oil yield and product quality.
Factory Site Selection and Infrastructure Planning for Coconut Oil Extraction Plant
Key Factors in Site Selection
Site selection determines both operational cost and long-term sustainability of a coconut oil extraction plant in the Philippines. Optimal plant locations typically balance raw material proximity, transportation networks, utility availability, and regulatory incentives. Based on data from the Department of Trade and Industry, Batangas, Davao, and Misamis Oriental offer attractive zones with established agro-industrial clusters.
Infrastructure and Utility Planning
A typical 250 TPD (tons per day) coconut oil extraction facility requires approximately 3–4 hectares of land, segmented as shown below:
| Facility Section | Area Allocation (m²) | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Yard | 4,500 | Copra unloading, pre-cleaning |
| Extraction Unit | 3,800 | Mechanical pressing, filtration |
| Refining Unit | 2,200 | Bleaching, deodorizing |
| Utility Section | 1,200 | Boilers, generators, cooling systems |
| Storage & Packaging | 2,500 |
Finished oil tanks, packaging lines |
Utility Requirements and Design Standards
The plant must ensure reliable access to 1.5 MW of electricity, 250 m³/day water supply, and compliant wastewater treatment facilities with a biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) limit below 50 mg/L. Infrastructure planning should also include redundancy systems for both power and water to mitigate downtime risks.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
The Department of Environment and Natural Resources (DENR) mandates adherence to ISO 14001 environmental management systems. Modern extraction plants often incorporate biomass boilers utilizing coconut shell waste, cutting fossil fuel dependency by 30–35%.
- Renewable Integration: Solar panels generating 200 kWh/day for lighting and auxiliary loads.
- Wastewater Reuse: Recycling 60% of treated effluent for cooling towers.
- Worker Welfare: Designing ergonomic workstations to meet local labor safety codes.
Proper land grading and stormwater management are critical to avoid contamination and operational delays during monsoon seasons.
Get your customized coconut oil extraction plant layout and infrastructure blueprint—contact our process engineers today.
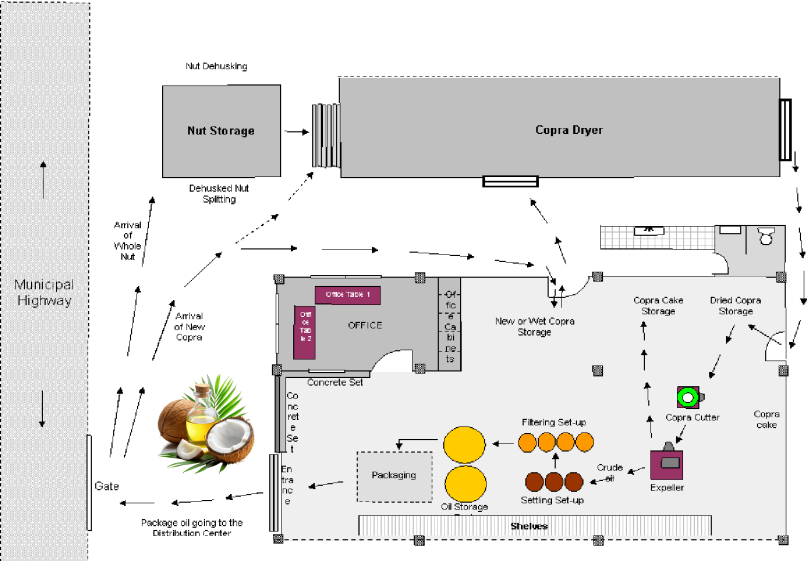
Coconut Oil Making Technical Route and Process Feasibility Analysis

Large Coconut Oil Mill Plant for Sale
Coconut oil extraction can be carried out using either dry process (copra-based) or wet process (fresh coconut-based). The dry process—yielding about 62% oil recovery—is widely adopted for industrial-scale operations due to its lower capital investment and ease of automation.
Energy efficiency is a key determinant of plant profitability. A standard expeller line consuming 45–55 kWh per ton of copra can be optimized using screw press modifications and heat recovery units, improving overall energy utilization by 12–15%.
Equipment configuration typically includes vibrating screens, coconut oil expeller machine, plate filters, vacuum dryers, and centrifugal separators. Integrating MES (Manufacturing Execution System) allows real-time monitoring of throughput, downtime, and batch traceability.
The wet process, though yielding slightly higher-quality virgin coconut oil (VCO), incurs higher operational costs—about 25% more energy input and 40% higher water usage. For large-scale export operations, dry extraction combined with solvent recovery systems remains the most cost-effective approach.
Partner with us to implement an energy-efficient coconut oil extraction process that maximizes yield while reducing operational costs.
In conclusion, establishing a modern coconut oil extraction plant in the Philippines represents a viable industrial opportunity supported by strong raw material availability, government incentives, and global demand growth. From plant site design to process optimization, every engineering step must align with sustainability, efficiency, and profitability goals—ensuring competitiveness in the international coconut oil market.
coconut oil extraction continues to anchor agricultural-industrial synergy in the Philippines, strengthening its global leadership in natural oil exports.
We receive enquiries in English, Español (Spanish), Русский язык (Russian), Français (French) and العربية (Arabic).Our professional team will reply to you within one business day.Please feel free to contact us!



 Screw Oil Press
Screw Oil Press Small Oil Mill Plant
Small Oil Mill Plant Small Oil Refinery
Small Oil Refinery Automatic Oil Press
Automatic Oil Press Multifunction Oil Press
Multifunction Oil Press Hydraulic Oil Press
Hydraulic Oil Press


![[Presidential Visit] Zimbabwe 30 Tons/Day soybean oil plant for Extraction and Refinery Was Successfully Completed](/uploads/allimg/soybean-oil-plant-press-refine-business-lp.jpg)

